This voyage is made possible through the art and science of Data Mining in Business Analytics, a fascinating journey. So, grab your virtual pickaxe, and let’s start mining for insights!
Unearthing the Basics: What is Data Mining?
Data mining, often referred to as knowledge discovery in databases (KDD), is the process of extracting hidden patterns, trends, and valuable information from large datasets. It’s akin to sifting through a mountain of sand to find the rare gems.
Here are a few links that give better understanding on data mining:
https://www.javatpoint.com/data-mining
Data Mining vs. Traditional Data Analysis
Imagine data mining as a skilled detective, searching for hidden clues in the dark corners of data, whereas traditional data analysis is more like a casual observer, only scratching the surface. Data mining digs deep and uncovers the concealed stories.
The Tools of the Trade: Data Mining Techniques
- Classification for Predictive Analysis Think of this as the sorting hat in the world of Harry Potter, but instead of houses, it categorizes data into classes. We use it to make predictions about future data based on past observations.
- Clustering for Pattern Discovery Like a detective solving a jigsaw puzzle, clustering groups similar data points together, helping us identify hidden patterns and relationships.
- Association Rule Mining for Market Basket Analysis This is the Sherlock Holmes of data mining, uncovering associations between products in a shopping basket, helping businesses make strategic decisions.
- Anomaly Detection: Finding the Odd One Out Just like spotting a needle in a haystack, anomaly detection helps us identify unusual patterns or data points in a sea of normality.
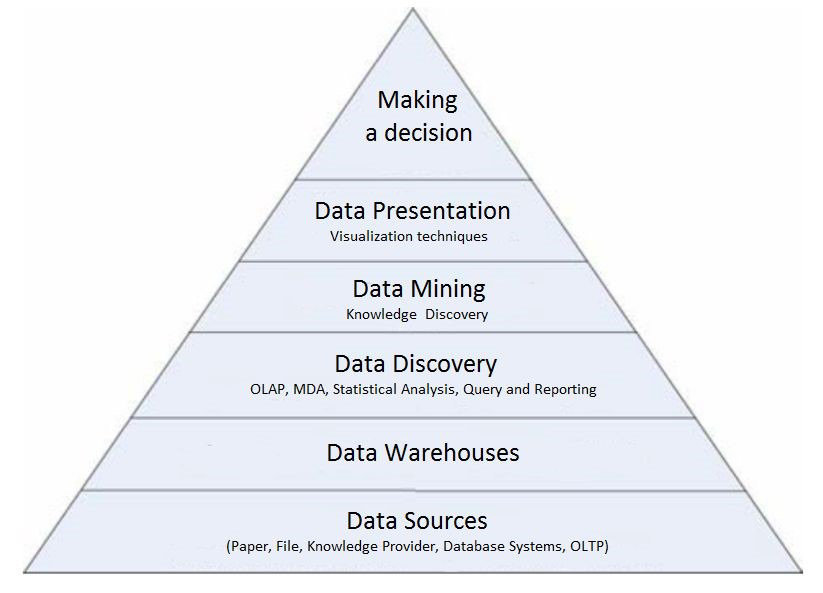
Challenges in Data Mining
- Data Quality Imagine mining for gold, but the soil is mixed with impurities. Poor data quality can lead to erroneous insights, just as impurities affect the purity of gold.
- Overfitting It’s like trying to make a dress that fits every customer. Overfitting occurs when a model is too complex, fitting the training data perfectly but failing to generalize well.
- Interpretability Data mining models can be as intricate as a spider’s web. Ensuring that they are interpretable is crucial, so decisions are made with confidence.
Conclusion: Navigating the Data Minefield
In this journey, we’ve delved into the captivating world of data mining in business analytics. It’s like exploring a treasure chest of insights, where every data point is a hidden gem. With the right tools, techniques, and ethical principles, businesses can unlock a world of possibilities and create a brighter future.
Feel free to reach out if you need any further adjustments or if you have any other specific requirements.



